
For example, during apoptosis (programmed cell death), the outer monolayer of the plasma membrane exhibits lipids that are typical of the inner monolayer. membrane invaginations are easier toward the cytosol.ĭ isorganization of the membrane asymmetry usually brings damages to the cell. For example, in the plasma membrane, it is thought that it is easier the formation of vesicles toward the cytosol, i.e.
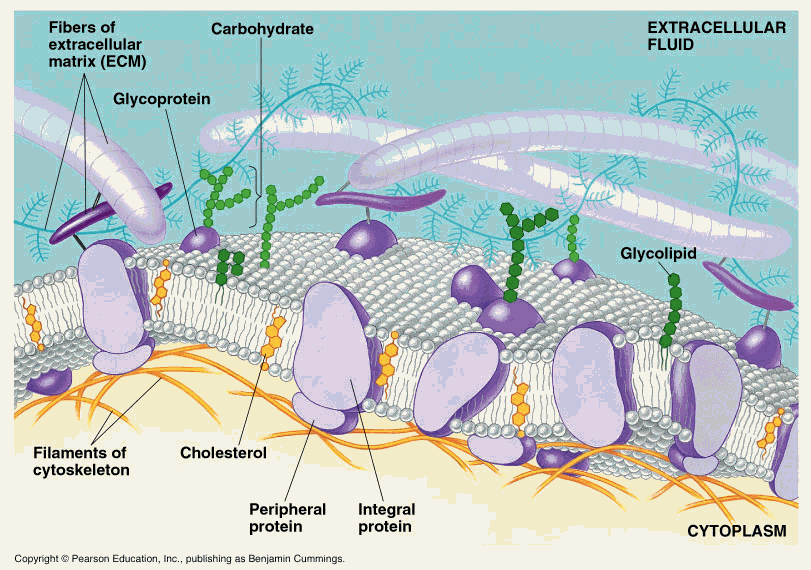
The membrane asymmetry also provides physical properties to membranes. Furthermore, carbohydrates are located in the outer monolayer of the plasma membrane, contributing to the asymmetry.
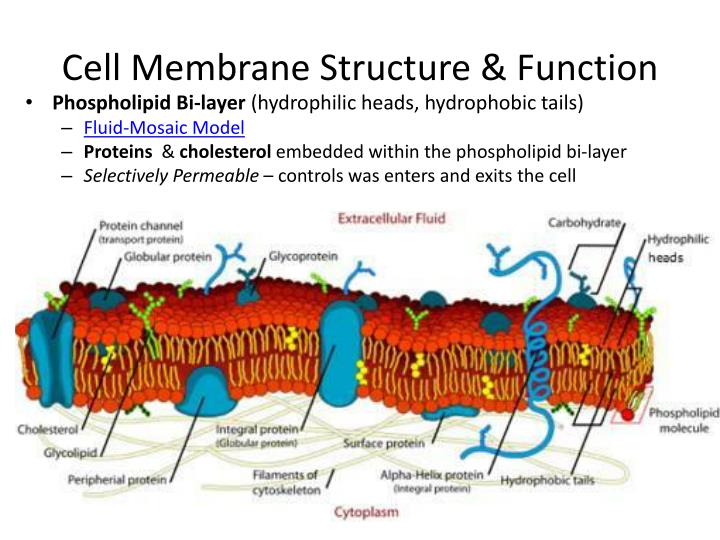
For example, phosphatidylinositol is mostly located in the inner monolayer of the plasma membrane and can be split into two molecules by some phospholipases then one of the two molecules travels through the cytosol working as a second messenger. The location of some lipids in a particular monolayer is important in this respect. Furthermore, it allows the association of specific proteins with a particular surface of the membrane due to the distinct environment created by the electro-chemical properties of lipid heads, which are different between both sides. This is useful for the cell because it sets an unequal electrical charges distribution at both sides of the membrane, which helps to generate the membrane potential. For example, in the plasma membrane, the outer monolayer contains most of the lipids having choline, such as phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin, whereas the inner monolayer contains more phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylserine. It is essential for the cell to generate and maintain membrane asymmetry. This unequal distribution of molecules between both monolayers is referred as membrane asymmetry, and was known even before the fluid mosaic model of membrane was proposed in 1972. Moreover, transmembrane proteins are placed in the membrane with a precise orientation. Lipids, carbohydrates and peripheral proteins are present in different types and proportions when both monolayers are compared. In plasma and organelle membranes there is one monolayer facing the extracellular space or the lumen of the organelle, respectively, whereas the other monolayer usually faces the cytosol. Meiosis ◂ More information Cellularity A Leeuwenhoek Discovering cell division ARN world Cell size Hyaluronic acid Cell wall More than adhesion Membrane models Gap junctions Plasmodesmata Condensins y cohesins Chromosomes Autophagy Vesicles Transcytosis Extracellular vesicles Centriole / basal body Cilia and flagella Microvilli Cell cycle regulation Centrosome cycle Apoptosis QuizzesĬell membranes are made up of two lipid monolayers. Cell cycle G1 phase S phase G2 phase M phase. Cytosol Cytoskeleton Actin filaments Microtubules Intermediate filaments 8.

Non vesicular Peroxisomes Mitochondria Plastids Chloroplasts Lipid droplets 7. Vesicular trafficking Endoplasmic reticulum From reticulum to Golgi Golgi apparatus Exocytosis Endocytosis Endosomes Lysosomes In plant cells Vacuoles 6.
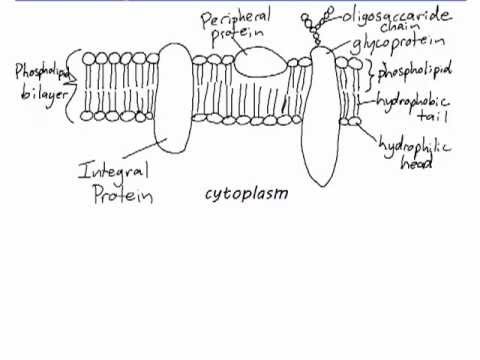
Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nuclear pore Chromatin Nucleolus 5. Cell membrane Lipids Proteins Carbohydrates Permeability, fluidity Asymmetry, repairing Synthesis Transport Adhesion Cell junctions 4. Extracellular matrix Structural proteins Carbohydrates Glycoproteins Types 3. Introduction Cell diversity Discovery of cells Cell theory Origin of the cell Origen of eukaryotes Endosymbiosis 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
